Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. This infection affects both men and women, though it is more commonly diagnosed in women. Trichomoniasis can lead to discomfort, increased susceptibility to other STIs, and complications if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention.
Causes and Transmission
Trichomoniasis spreads primarily through sexual contact, including vaginal intercourse. The parasite is transmitted from an infected person to a non-infected partner. It does not spread through oral or anal sex, and non-sexual transmission (such as through toilet seats or shared towels) is highly unlikely.
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis
Many individuals infected with Trichomonas vaginalis do not exhibit symptoms, making early detection challenging. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
In Women:
- Vaginal itching or irritation
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge (yellow-green or frothy)
- Painful urination
- Discomfort during intercourse
- Lower abdominal pain (in severe cases)
In Men:
- Irritation or burning after urination or ejaculation
- Discharge from the penis
- Mild itching inside the penis
Since the symptoms of trichomoniasis can resemble those of other infections, such as bacterial vaginosis or yeast infections, proper medical evaluation is necessary.
Diagnosis
Trichomoniasis is diagnosed through laboratory tests that detect the presence of Trichomonas vaginalis. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Microscopic examination of vaginal or urethral secretions
- Rapid antigen tests
- Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), which are highly sensitive
- Culture tests, though less commonly used today
Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmitting the infection to sexual partners.
Treatment Options
Trichomoniasis is treatable with prescription medications, primarily antibiotics. The most common medications used are:
- Metronidazole (Flagyl) – A widely prescribed oral antibiotic effective against Trichomonas vaginalis.
- Tinidazole (Tindamax) – Similar to metronidazole but may cause fewer side effects.
- Nizonide – Though primarily used to treat other parasitic infections, some studies have explored its effectiveness against trichomoniasis due to its antiparasitic properties.
Patients should complete the full course of antibiotics even if symptoms resolve early. Alcohol consumption should be avoided while taking these medications, as it can cause severe nausea and vomiting.
Prevention Strategies
Since trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection, taking preventive measures is crucial:
- Use of condoms during intercourse to reduce the risk of transmission.
- Limiting the number of sexual partners and maintaining a monogamous relationship.
- Regular STI screenings, especially for sexually active individuals.
- Prompt treatment of infected individuals and their partners to prevent reinfection.
Complications of Untreated Trichomoniasis
If left untreated, trichomoniasis can lead to several health complications, including:
- Increased susceptibility to HIV and other STIs.
- Pregnancy-related complications, such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, leading to long-term reproductive health issues.
Trichomoniasis and Nizonide: An Emerging Treatment Option?
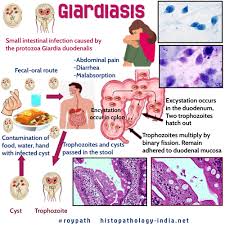
The nizonide, also known as nitazoxanide, is an antiparasitic medication traditionally used to treat infections like giardiasis and cryptosporidiosis. Some research suggests that Nizonide may have potential efficacy against Trichomonas vaginalis, although it is not currently a first-line treatment for trichomoniasis. More clinical studies are needed to determine its effectiveness and safety profile in treating this specific STI.
Conclusion
Trichomoniasis is a widespread but treatable infection. Awareness, regular screening, and safe sexual practices are crucial for prevention. While traditional antibiotics remain the standard treatment, emerging alternatives like Nizonide may hold promise for future treatment options. If you suspect an infection, seeking timely medical advice and completing the prescribed treatment is essential for overall health and well-being.