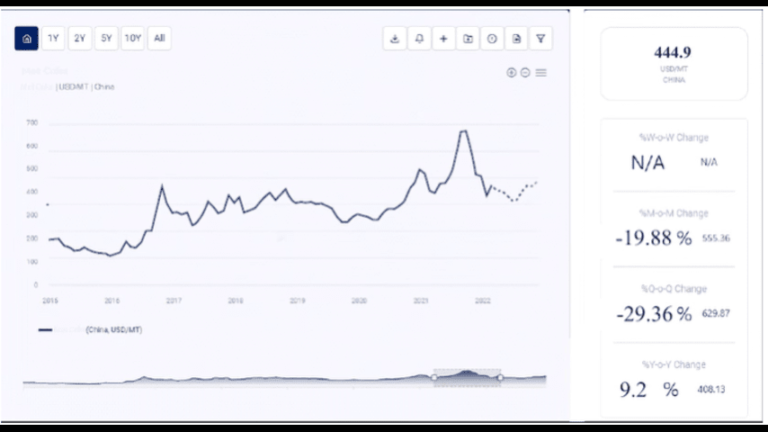
Cotton is one of the most important agricultural commodities, playing a pivotal role in the global textile industry. It is used to produce a wide variety of products, including clothing, home textiles, and industrial materials. The price of cotton is highly volatile and influenced by various factors such as weather conditions, global supply-demand dynamics, government policies, and market speculation. Understanding the cotton price trend is crucial for farmers, textile manufacturers, investors, and businesses involved in its supply chain.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of the factors influencing cotton prices, historical price trends, and insights into future projections. For stakeholders in the cotton industry, understanding these trends is essential for making informed decisions about procurement, production, and market strategies.
1. Overview of Cotton
What is Cotton?
Cotton is a natural fiber derived from the cotton plant, which thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. It is a crucial raw material for the textile industry and is known for its softness, breathability, and versatility. Cotton is grown in several major producing regions, including the United States, China, India, Pakistan, and Brazil.
Applications of Cotton
Cotton is used in a wide variety of products, including:
- Textiles and Apparel: The largest portion of cotton production is used to make clothing, bed linens, towels, and other textile products.
- Home Furnishings: Cotton is widely used in the production of curtains, upholstery, and other home décor items.
- Industrial Products: Cotton fibers are used in making industrial materials such as medical supplies, absorbent products, and even paper.
- Cottonseed Oil: A byproduct of cotton production, cottonseed oil is used in food products, cosmetics, and as a raw material for biofuels.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/cotton-price-trends/pricerequest
2. Factors Influencing Cotton Price Trends
Several key factors directly influence the price of cotton, ranging from weather patterns and global demand to government policies and speculative activities. Understanding these factors is crucial for anticipating price movements and making strategic decisions.
a. Supply and Demand Dynamics
As with most commodities, cotton prices are influenced by the balance between supply and demand. Any changes in global cotton production, consumer demand, or textile manufacturing activities can cause price fluctuations.
- Global Demand: Cotton demand is driven primarily by the textile industry. When consumer demand for clothing and textiles increases, especially in regions like China, India, and the United States, it leads to higher demand for raw cotton, pushing prices upward. Conversely, reduced demand can lower prices.
- Production Levels: The supply of cotton is largely dependent on production levels in major growing regions. If cotton yields are affected by unfavorable weather conditions, pest infestations, or water shortages, the resulting supply shortfall can cause prices to rise.
b. Weather and Climate Conditions
Cotton is highly sensitive to weather conditions, and any disruptions in major producing regions can lead to price volatility. Droughts, floods, or excessive rainfall can significantly impact cotton yields.
- Droughts and Water Scarcity: Cotton is a water-intensive crop, and droughts or water shortages in key producing regions can lead to reduced yields. This can result in supply shortages and drive up cotton prices.
- Extreme Weather Events: Hurricanes, floods, and other extreme weather events can damage crops and disrupt supply chains, causing sudden spikes in cotton prices.
c. Government Policies and Trade Agreements
Government interventions, such as subsidies, tariffs, and export restrictions, can significantly affect cotton prices. In addition, international trade agreements play a critical role in determining the flow of cotton between countries.
- Subsidies: Many cotton-producing countries, such as the United States and China, offer subsidies to support their domestic cotton industries. These subsidies can influence production levels and affect global prices by making domestic cotton more competitive.
- Tariffs and Trade Policies: Trade policies, including tariffs on cotton imports or exports, can impact prices by either increasing or reducing the cost of cotton for international buyers and sellers. For example, during the U.S.-China trade war, tariffs on cotton affected the global cotton trade and price volatility.
d. Global Economic Conditions
The overall health of the global economy also affects cotton prices. When the economy is growing, demand for textiles and apparel rises, boosting demand for cotton. Conversely, during economic downturns, demand for cotton tends to decrease.
- Economic Growth: In periods of economic expansion, the textile and apparel industries thrive, leading to higher demand for cotton and increased prices.
- Recessions: Economic downturns often lead to reduced consumer spending on apparel and home textiles, causing a drop in demand for cotton and lower prices.
e. Market Speculation and Investor Sentiment
Cotton prices are also influenced by market speculation and investor sentiment in commodities markets. Speculators buy and sell cotton futures contracts based on their expectations of future prices, which can cause short-term price swings.
- Futures Contracts: Cotton futures contracts allow traders to buy or sell cotton at a predetermined price in the future. Speculative activity in these contracts can amplify price movements, particularly when unexpected events occur in the cotton market.
- Commodity Markets: Like other agricultural commodities, cotton is traded on global exchanges such as the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) and the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE). Price fluctuations in these markets can be driven by speculation and market sentiment.
f. Technological Advancements and Sustainability
Technological advancements in cotton farming, such as the use of genetically modified (GM) cotton seeds, improved irrigation techniques, and precision farming, can influence both the supply and cost of cotton production.
- Genetically Modified Cotton: GM cotton varieties are engineered to be resistant to pests and diseases, leading to higher yields and lower production costs. The widespread adoption of GM cotton has increased global supply, contributing to price stability in some regions.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Growing awareness of environmental sustainability has led to a rise in demand for organic cotton and sustainable farming practices. While organic cotton often commands higher prices, the push for sustainable farming can impact the overall supply and cost structure in the industry.
3. Historical Price Trends of Cotton
a. Pre-2020 Stability
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, cotton prices generally followed a cyclical pattern based on global demand, weather conditions, and economic factors. Prices were relatively stable, with fluctuations influenced by seasonal changes and trade policies.
- 2010-2020: Cotton prices fluctuated between $0.60 and $1.00 per pound, depending on production levels and demand from major consuming regions like China and India. Prices were largely stable, with some volatility caused by trade disputes and natural disasters in key producing areas.
b. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic (2020-2021)
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on global cotton markets, causing prices to experience significant volatility. As countries implemented lockdowns and restricted trade, the textile industry faced disruptions that affected both supply and demand for cotton.
- Demand Collapse in 2020: The initial impact of the pandemic led to a collapse in demand for textiles and apparel as retail stores closed and consumer spending fell. This caused cotton prices to drop sharply in early 2020.
- Recovery and Price Surge in 2021: By mid-2021, as economies reopened and consumer demand for clothing rebounded, cotton prices surged. Supply chain disruptions, combined with strong demand from textile manufacturers, led to significant price increases.
c. Post-Pandemic Recovery (2022-Present)
As global economies recover from the pandemic, cotton prices have stabilized, though they remain influenced by inflationary pressures, supply chain disruptions, and ongoing changes in consumer demand.
- Strong Demand for Textiles: The post-pandemic recovery in consumer spending on apparel and home goods has supported strong demand for cotton, contributing to price stabilization.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Ongoing supply chain disruptions, including shipping delays and labor shortages, continue to impact cotton prices, especially in regions reliant on imports of cotton or cotton products.
4. Future Price Forecast for Cotton
Several factors will shape the future price trends for cotton, including environmental concerns, economic recovery, and technological advancements.
- Sustainable Cotton Farming: As sustainability initiatives gain momentum, there may be a shift toward organic cotton and more environmentally friendly farming practices. This could lead to supply constraints in conventional cotton and drive up prices for sustainable cotton products.
- Global Demand Growth: Demand for cotton is expected to remain strong as global populations grow and disposable income increases, particularly in developing economies. The expansion of the middle class in Asia and Africa will drive demand for clothing and textiles, supporting higher cotton prices.
- Weather-Related Risks: The increasing frequency of extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, will continue to pose risks to cotton supply, potentially leading to price volatility in the coming years.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Numbers:
- USA & Canada: +1 307 363 1045
- UK: +44 7537171117
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA