Natural rubber, derived from the latex of rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), is an essential raw material in many industries, particularly for the production of tires, footwear, industrial goods, and a variety of consumer products. Its unique physical properties—such as elasticity, tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion—make it indispensable in automotive, construction, and manufacturing sectors.
Over the years, the natural rubber price trend has exhibited significant volatility, driven by a complex interplay of factors including supply-demand dynamics, weather conditions, production costs, and global economic trends. For businesses reliant on natural rubber, understanding these price trends is crucial for effective procurement strategies, cost management, and long-term planning.
In this article, we will explore the historical and recent price trends of natural rubber, analyze the key factors influencing its market value, and assess the future outlook for this vital commodity.
1. Overview of Natural Rubber Production
Before diving into the price trends, it’s important to understand the global production landscape of natural rubber.
a) Major Producers
- Southeast Asia’s Dominance: Natural rubber is primarily grown in tropical regions, with Southeast Asia being the dominant producer. Countries like Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, Malaysia, and India account for more than 80% of global natural rubber production. Thailand is the largest producer, contributing about one-third of the world’s supply.
- Smallholder Farming: In many producing countries, the majority of rubber cultivation is carried out by smallholder farmers, making the sector highly fragmented. This leads to challenges in terms of productivity, quality control, and vulnerability to price fluctuations.
- Synthetic vs. Natural Rubber: It’s also important to note that natural rubber competes with synthetic rubber, which is derived from petroleum-based products. While synthetic rubber is used for certain applications due to its lower cost and consistent quality, natural rubber remains irreplaceable in high-performance applications like aircraft tires and medical gloves.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/natural-rubber-price-trends/pricerequest
b) Harvesting and Seasonality
Rubber tapping, the process of extracting latex from trees, is a labor-intensive activity and is heavily dependent on favorable weather conditions. Rubber trees need stable temperatures and high humidity to thrive, and production can be disrupted by factors such as heavy rainfall, droughts, or disease outbreaks. These seasonal and environmental variables contribute to the cyclicality and volatility of natural rubber supply.
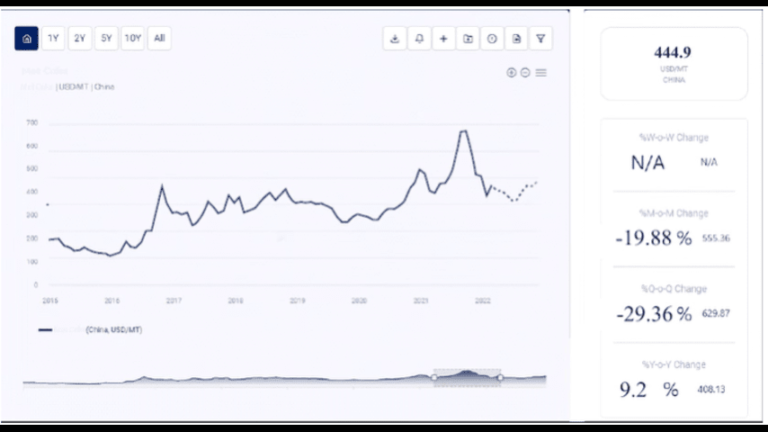
2. Historical Price Trends of Natural Rubber
The natural rubber market has seen several boom-and-bust cycles over the past few decades. Prices have fluctuated due to a variety of factors, including changes in demand from the automotive industry, shifts in production, and external shocks such as natural disasters or geopolitical events.
a) The Early 2000s
- Steady Demand Growth: In the early 2000s, natural rubber prices remained relatively stable as global demand, particularly from the automotive industry, grew steadily. Emerging markets, especially China and India, began to consume more rubber due to the rapid expansion of their automotive and industrial sectors.
- Supply Challenges: During this period, rubber-producing countries faced sporadic supply challenges due to adverse weather conditions, which temporarily pushed prices higher. However, improved production techniques and the expansion of rubber plantations in Southeast Asia helped balance supply and demand.
b) Price Surge During 2008-2011
- Commodity Boom: Between 2008 and 2011, natural rubber prices surged dramatically, peaking at record highs. Several factors contributed to this price spike:
- Global Economic Growth: In the years leading up to the global financial crisis, strong demand from emerging markets, particularly China, fueled a commodity boom. Natural rubber, being a key input for the automotive industry, saw demand soar.
- Supply Constraints: Unfavorable weather conditions, including heavy rains and flooding in Southeast Asia, hampered rubber production, leading to a supply shortage. At the same time, speculative trading in commodity markets exacerbated price volatility.
- Oil Price Surge: The concurrent rise in oil prices during this period also had an impact on natural rubber prices. As the cost of synthetic rubber, derived from petroleum, increased, manufacturers turned to natural rubber as an alternative, further boosting demand.
c) Post-2011 Decline and Stabilization
- Global Economic Slowdown: After peaking in 2011, natural rubber prices began to decline sharply, driven by the global economic slowdown following the financial crisis. Demand from key markets, particularly the automotive sector, weakened, causing a significant drop in prices.
- Oversupply Issues: At the same time, rubber-producing countries had expanded their plantations during the price boom years, leading to an oversupply of natural rubber. As a result, prices continued to fall as the market struggled to absorb the excess production.
- Currency Depreciation: The depreciation of currencies in major rubber-producing countries (such as the Thai baht and the Indonesian rupiah) during this period also contributed to lower global prices, as rubber became cheaper in dollar terms.
3. Recent Natural Rubber Price Trends (2020-2023)
In recent years, natural rubber prices have experienced renewed volatility, influenced by a combination of global economic factors, supply chain disruptions, and changing demand patterns.
a) The Impact of COVID-19
- Pandemic-Induced Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on the natural rubber market. During the initial phase of the pandemic in 2020, global demand for rubber products, particularly from the automotive sector, plummeted as economies went into lockdown. As a result, natural rubber prices dropped to multi-year lows.
- Supply Chain Challenges: However, the pandemic also caused significant disruptions to global supply chains, particularly in shipping and logistics. Rubber-producing countries faced labor shortages due to lockdowns and travel restrictions, which slowed down production and export operations. This created temporary supply shortages, leading to a rebound in prices by late 2020.
- Increased Demand for Medical Gloves: At the same time, the pandemic spurred a surge in demand for medical gloves and other personal protective equipment (PPE), which are made from natural rubber latex. This new demand segment helped support prices during a period of otherwise weak demand from traditional sectors.
b) Price Volatility in 2021-2022
- Recovery in Automotive Sector: As global economies began to recover from the pandemic, demand for natural rubber from the automotive industry rebounded in 2021 and 2022. The resumption of industrial activity and increased car sales, particularly electric vehicles (EVs), drove demand for tires and other rubber products, contributing to price volatility.
- Supply Chain Bottlenecks: Global supply chain bottlenecks, particularly in shipping and transportation, exacerbated price fluctuations. Delays in transporting rubber from Southeast Asia to major markets such as China, the U.S., and Europe led to temporary supply shortages, causing price spikes.
- Inflationary Pressures: Rising inflation, particularly in energy and labor costs, also contributed to upward pressure on rubber prices during this period. The increased cost of production in key rubber-producing countries translated into higher export prices.
c) Natural Rubber Prices in 2023
- Slight Decline Amid Economic Uncertainty: In 2023, natural rubber prices showed signs of softening compared to the previous year, largely due to growing concerns about a global economic slowdown. Weaker demand from the automotive industry, combined with economic uncertainties in key markets such as China and the U.S., has led to a slight decrease in prices.
- Supply Side Factors: On the supply side, favorable weather conditions in key producing regions have resulted in stable rubber output, helping to alleviate some of the supply constraints seen in previous years. However, the industry remains vulnerable to climate change and potential disruptions caused by extreme weather events.
4. Key Factors Influencing Natural Rubber Prices
Several factors continue to shape the natural rubber market, influencing both short-term price fluctuations and long-term trends.
a) Climate Change and Weather Conditions
- Vulnerability to Weather Events: Natural rubber production is highly dependent on weather conditions, making it vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Droughts, excessive rainfall, or disease outbreaks (such as the South American Leaf Blight) can significantly reduce yields, leading to supply shortages and price increases.
- Long-Term Climate Risks: In the long term, climate change poses a serious risk to natural rubber production. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events could threaten the viability of rubber plantations in traditional growing regions, leading to supply disruptions and higher prices.
b) Global Demand Dynamics
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry remains the largest consumer of natural rubber, particularly for tire production. Any fluctuations in global vehicle sales, particularly in emerging markets like China and India, can have a significant impact on natural rubber demand and prices.
- Growth of Electric Vehicles (EVs): The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to drive long-term demand for natural rubber, as EVs require high-performance tires with superior durability and lower rolling resistance. This could create new opportunities for the natural rubber market in the coming decades.
- Healthcare Sector: The healthcare sector is another important demand driver, particularly for latex products such as medical gloves. As global health infrastructure expands and the demand for healthcare products grows, this sector is expected to support long-term demand for natural rubber.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Number: USA & Canada — Phone no: +1 307 363 1045 | UK — Phone no: +44 7537 132103 | Asia-Pacific (APAC) — Phone no: +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA